
Natural gas is a combustible gaseous mixture of simple hydrocarbon compounds including methane, ethane, propane, butane and pentane. The principal constituent of natural gas is methane.
In its pure form, natural gas is colorless, odorless, tasteless and two times lighter than air. Natural gas is neither corrosive nor toxic. It has a high ignition temperature and a narrow flammability range, making it an inherently safe fossil fuel compared to other fuel sources.


Natural gas comes from organic remains of ancient plants and animals. The erosion process carried these biological remains down rivers and streams onto shorelines, where they are deposited along with mud and silt.
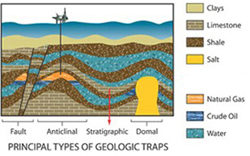
Overtime, sedimentary materials such as mud and sand cover the organic remains. Eventually the organic materials transform into petroleum products due to the intense pressure and heat present in the rock formation.
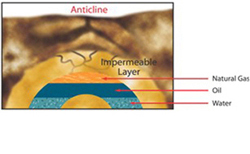
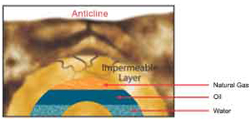
The oil and gas which migrate through the pores in the sedimentary rock eventually reach an impermeable layer of dense rock and collect in large deposits.

Natural gas is a vital component of the world’s supply of energy because of its economic and ecological advantages. When used to generate electricity in modern combine cycle gas turbines, it achieves an efficiency of 50 - 55% compared to 35 - 40% from a commercial fuel oil steam plant. This translates to cost savings for consumers of electricity in the industrial, commercial and residential sectors. Natural gas is also one of the cleanest and safest energy sources, producing mainly water vapour and lower carbon emissions compared to other fossil fuels. Burning of natural gas emits almost no sulphur into the atmosphere and is also a readily available source of competitive energy that is easily transported.
We advocate for natural gas as a cleaner fuel for power generation, domestic and commercial usages and as a transportation fuel.
Power Generators are increasingly using natural gas to provide energy for their power plants. Gas fueled power plants are more efficiently operated and emit less pollutants than other fossil fuel plants. Technological improvements in design and operation of combined cycle gas turbines and co-generation processes are the key driver of natural gas. A natural gas co-generation plant produces power and heat that is useful for industrial as well as commercial users. This co-generation reduces pollution emissions considerably.

There are myriad of ways for industrial applications of natural gas. These include feedstock, heating, cooling and industrial cooking. Natural gas is also used for waste treatment, incineration, metals preheating, drying and dehumidification, glass melting, food processing, fueling industrial boilers and pharmaceutical products. In plastics, pharmaceutical and recycling industries, natural gas desiccant systems are increasingly popular as it helps in the manufacturing or drying of the environment, allowing industrial users to better regulate the moisture in the air, leading to a more consistent and high-quality product.

Technology advancements have improved over the years to allow for a proliferation of natural gas vehicles. With stringent fuel emissions guidelines set in place to control environmental pollution, natural gas as the cleanest burning fuel is the most ideal option to meet emissions standards.
Natural gas can be used as a motor vehicle fuel in two ways: as compressed natural gas, which is the most common form and as liquefied natural gas. With heightened concerns around climate change and carbon emissions, countries are increasingly exploring natural gas as a fuel source.
Natural gas is mainly used for central air conditioning, refrigeration, heating and cooling in public and private commercial spaces, including office buildings, educational institutions, hotels and healthcare facilities.
Used in myriad of ways and in various sectors
Less combustible than other liquid fuels
Emits less carbon emissions
Co-generation and district-cooling
Customers can avoid large flammable inventory such as liquefied petroleum gas
© Gas Supply Pte Ltd 2021